I read a Frederic Delavier’s book « Strength Training Anatomy » and I learned good stuff.
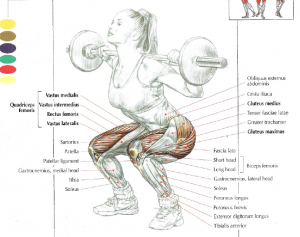
Squat is the #1 exercise for bodybuilding because it works a lot of the muscular system and is great for the cardiovascular system. Squat allows to have a good thoracic expansion and a good respiratory capacity.
-
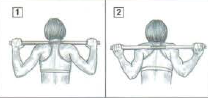
Standing in front of the barbell resting on the support. Put yourself under the barbell and place the barbell on your trapezius a little higher that the posterior deltoids. Take the barbell with a pronated grip. The spread of the hands is variable according to the morphology. Pull your elbows backwards.
-
Inhale deeply (to maintain an intrathoracic pressure that will prevent your torso from sagging forward). Arch you back slightly, squeeze your abs, look forward and take off the barbell.
-
Back 1 or 2 steps. Stop with your feet parallel (or slightly outward). Your feet are about your shoulders width. Squat down by tilting your back forward (the flexion axis passing through the hip joint). Control the descent without rounding your back to avoid injury.
-
When your femurs arrive horizontally, do an extension of your legs by straightening your torso to return to the starting position. Exhale at the end of the movement.
Squat works mainly quadriceps, glutes, adducteurs, erector spinae, abs and hamstring.
Note
Squat is one of the best moves to develop the gluteal curve.
2 ways to place the barbell
-
On trapezius
-
On deltoids and trapezius like powerlifters
Variants
-
People with stiff ankles or long femurs can place a wedge under the heels to avoid too much torso inclinaison. This allows to postpone a part of the effort on quadriceps.
-
The barbell’s position may be on the back (on the posterior deltoids). This reduce the cantilever by increasing the lifting power of the back which allows to take heavier weights. This is a technique used by powerlifters.
-
It’s possible to do squat with the Smith machine, which makes it possible to avoid the torso inclinaison and to locate the effort on quadriceps.
How to place the feet
The feet position is important during the execution of the classic squat (feet apart at about the shoulders width). Feet should be in parallel or slightly outward. What is most important is to respect the person’s morphology and to place the feet in the physiological axis of the knees. For example, if you walk with your feet out, squat with your feet out.
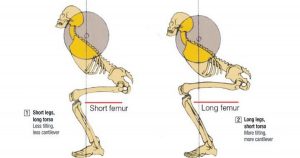
Different torso’s inclinaison according to the morphologies
-
Short legs, long torso : slightly inclined torso, weak cantilever
-
Long legs, short torso : very inclined torso, important cantilever
Good position
During the squat, the back should be as straight as possible throughout the movement. According of the morphologies (long/short legs, stiff/flexible ankles) and the different execution’s technique (feet’s position, use of compensated sole, barbell in up/down position), the torso could be very inclined or slightly inclined because flexion is done at the hip joint.
Bad position
It’s necessary not to round the back while performing the squat because this can create injuries in the lumbar region and spinal disc herniation.
Note
To really feel the work of the glutes, it’s necessary to have the thighs horizontally.
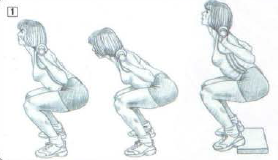
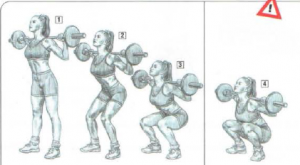
1-2-3 : negatives phase
4: full squat
It’s possible to have thighs lower than horizontal to better feel the glutes work but this technique can be done only by people who have short femurs or flexible ankles. It’s necessary to be very careful with the full squat because it is really easy to round the back.
Attention
For all exercises done with very heavy weight, it’s necessary to perform a « blocking » :
-
Take a deep breath and block the breathing to fill the lungs like a balloon. This stiffens the ribcage and prevents the top of the torso form tilting forward.
-
Squeeze abs stiffens the belly, This increases the intra-abdominal pressure and prevents the torse form sagging forward.
-
By slightly arching the lower back with lumbar squeeze, this allows to have the spine’s bottom in extension.
These 3 simultaneous actions is what we call « blocking ». This « blocking » has the function of avoiding the rounding or bending of the spine because with very heavy weights, it can create disc herniations .
Subscribe to my newsletter and share this article if you think it can help someone you know. Thank you.
-Steph