What’s up ? This is THE stephane ANDRE. With my training, I’m interested in biomechanics to avoid injuries. I read « Sport Medicine Media Guide » and I learned some good stuff.
There are 2 types of injuries : Acute injuries and overuse injuries. Acute injuries are usually caused by a single traumatic event. Here are some examples :
-
Wrist fractures
-
Ankle sprains
-
Shoulder dislocations
Acute injuries are less common in sport than overuse injuries. Overuse injuries are usually subtle and appear over time, making them difficult to diagnose and treat. Here is some example :
-
Tennis elbows
-
Swimmer’s shoulder
-
Pitcher’s elbow
-
Runner’s knee
-
Achilles tendinitis
-
Shin splints
Why
Human body is extraordinary to adapt to physical stress. We’re used of thinking that « stress » is bad for our emotional well-being, but physical stress is simply doing an exercise or activity. This is beneficial for our muscles, tendons, ligaments and bones. This physical stress causes an internal process called remodeling. Remodeling process involves both the breakdown and the build up of tissue. It’s necessary to have a good balance between 2, if breakdown occurs more rapidly than buildup, an overuse injury occurs.
Causes
Usually, it’s training errors that cause overuse injuries. These errors are too fast acceleration of intensity or duration or activity frequency. These injuries can also happen to people who return to the sport/activity after an injury. They try to make up for lost time as quickly as possible to reach the level they had before the injury. Doing an exercise with a good technique is important to avoid overuse injuries. When the exercise’s technique is bad, it creates overuse injuries. It’s for this reason that coaches, athletic trainers and teachers can play a preventive role so that athletes avoid overuse injures.
There are people who more easily have overuse injuries. An unbalance between strength and flexibility around certain joints predisposes some people to have this type of injury. Body alignment, such as knock-knees, bowlegs, unequal leg lengths and flat or high arched feet, also impact overuse injuries. There are also people who have weak links because of old wounds, incomplete rehabilitation of wounds or others anatomy factors.
Other factors must also be taken into account as equipment such as the type of running shoe or ballet shoe and terrain (hard versus soft surface in aerobic dance or running).
Diagnosis
Generally the diagnosis is based on the athlete’s history and physical examination. It’s recommended to make a diagnosis with a sports medicine specialist with a specific interest and knowledge of your sport. In some situations X-rays, bone scan and MRI may be necessary.
Treatment
Here are some recommendations for treating an overuse injuries :
-
Cutting back the intensity, duration and frequency of an activity
-
Adopting a hard/easy workout schedule and crosstraining with other activities to maintain fitness levels
-
Learning about proper training and technique from a coach or athletic trainer
-
Performing proper warm-up activities before and cool down after
-
Using ice after an activity for minor aches and pain
-
Using anti-inflammatory medications as necessary
If symptoms persist, a sport medicine specialist may create a more detailed treatment plan for your specific condition. This may involve an exam of your training program and an evaluation of predisposing factors.
Prevention
Majority of overuse injuries can be avoided with a proper training program, common sense and learning to listen your own body. The quote : « No pain, no gain » doesn’t apply here. The 10% rule helps a lot to get things to the next level.
In general, you should increase the training’s intensity to a maximum of 10% per week. This allows your body to have enough time for recovery and response. This rule should be used to increase pace or milestone for walkers or runners. Or for the weights amount to increase for strength training programs. In strength training, add flexibility exercises and core stability exercises help tremendously to minimize overuse injuries.
It’s recommended to seek advice from sports medicine specialist or athletic trainer to prevent chronic or recurring problems. Your training program can also be modified to maintain fitness levels safety while you recover from your injuries. You must return to the sport only if an authorization is granted by a health professional.
Remember, it’s very important to warm-up before training and cool down after training.
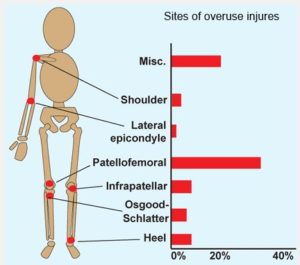
Stats
3.5 millions of children are treated for overuse injures every year.
Subscribe to my newsletter and share this article if you think it can help someone you know. Thank you.
-Steph
P.S. If you’re in Miami and you like Caribbean food, go to my cousin’s bistro to eat Haitian food. Click here .